The IUC-Asia programme held an online session today to present its progress on the ongoing EU-China Low Carbon City Study, along with case studies of several cities. On the call were senior experts from both China and Europe. The study is being jointly drafted by the IUC-Asia project and experts of China’s National Center for Climate Change Strategy and International Cooperation (NCSC). Today’s online session was a stepping stone to the onsite conference foreseen for September 2020 in China (TBC).
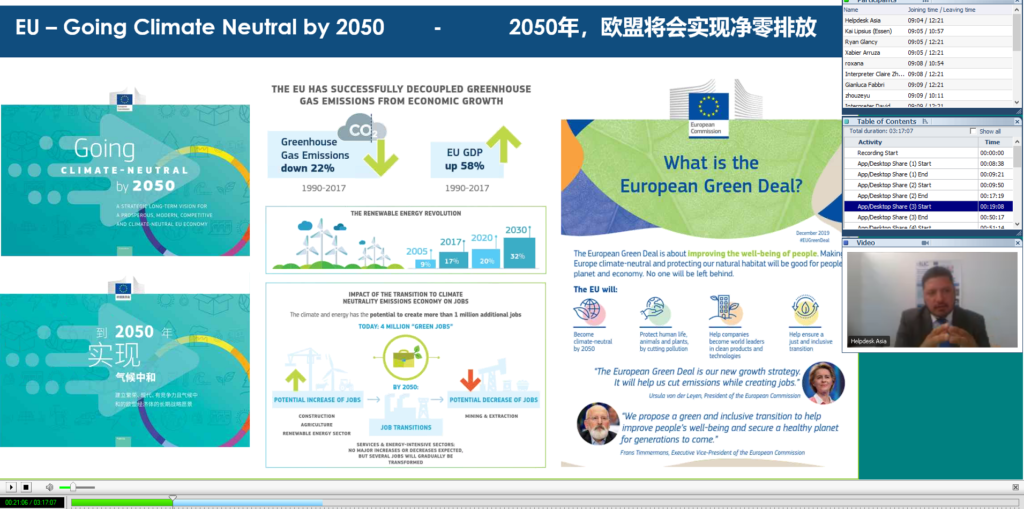
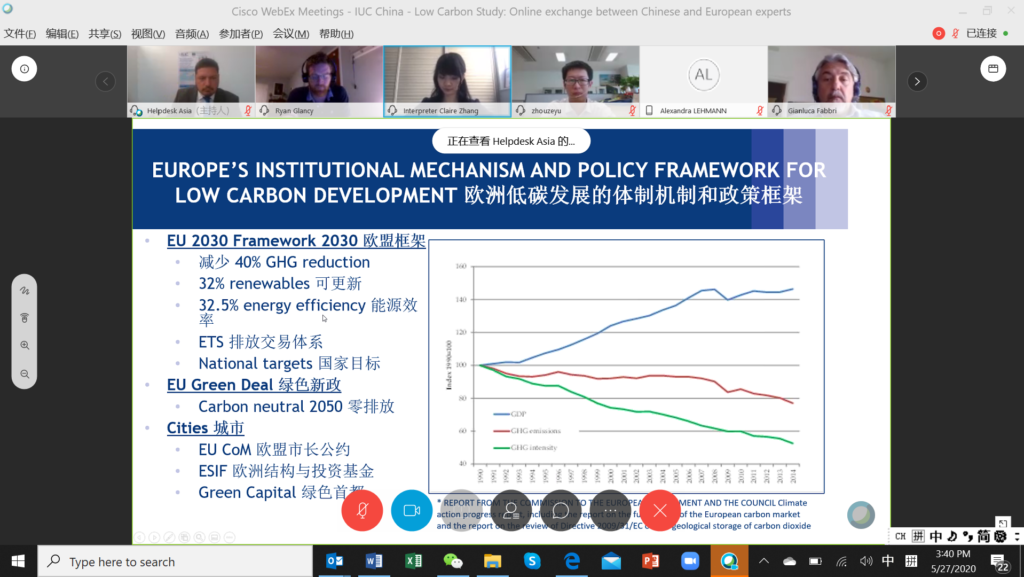
During the call, the authors of the study and senior experts from the Chinese and European cities and provinces discussed the study. They explained: the main GHG emissions sources; ongoing programmes at national, provincial and local level to mitigate the emissions; achievements, challenges and future goals. The discussion also dealt with the implications of the European Union’s Green Deal for the transition towards low carbon in European cities as well as with the possible implications of China’s 14th Five Year Plan for Chinese local authorities.
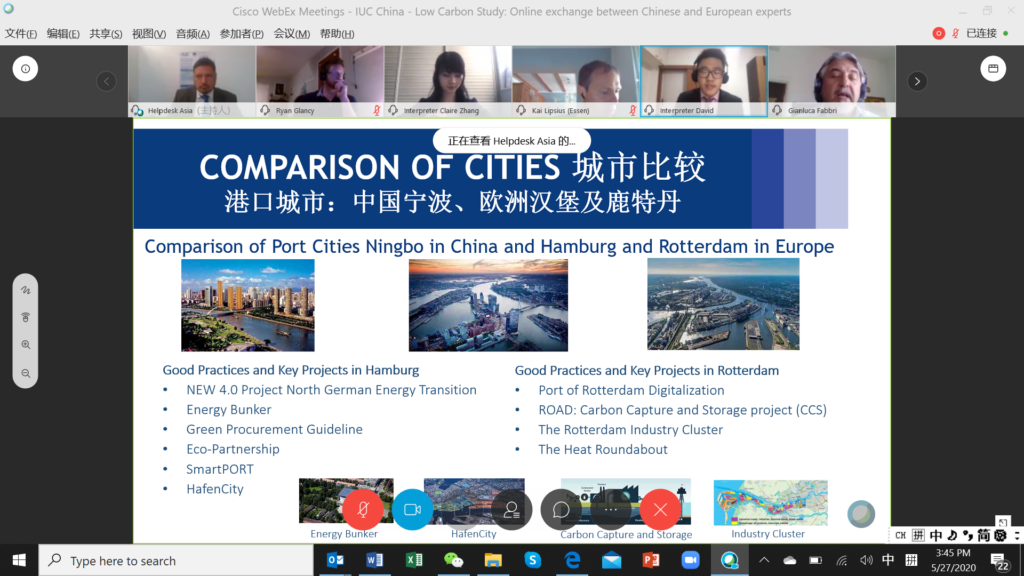
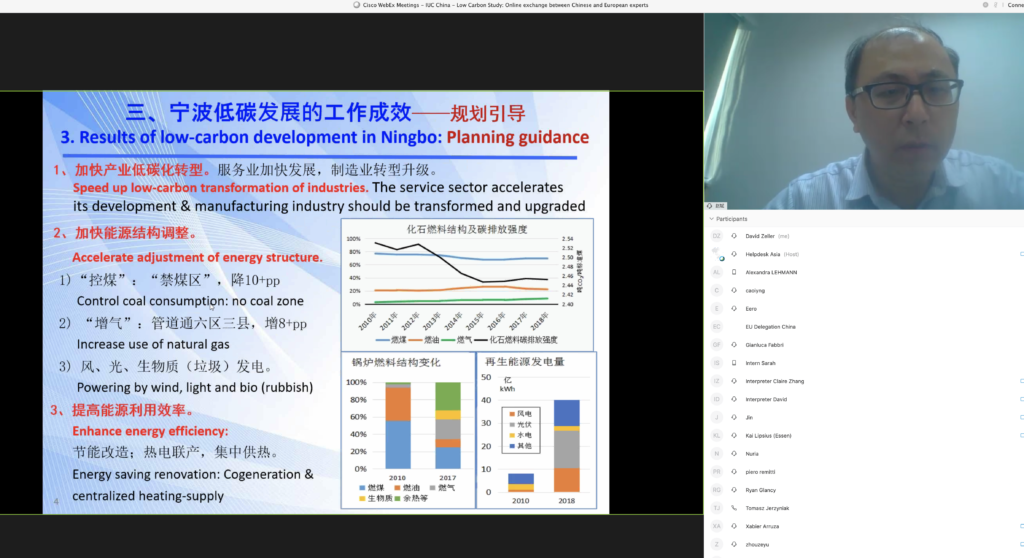
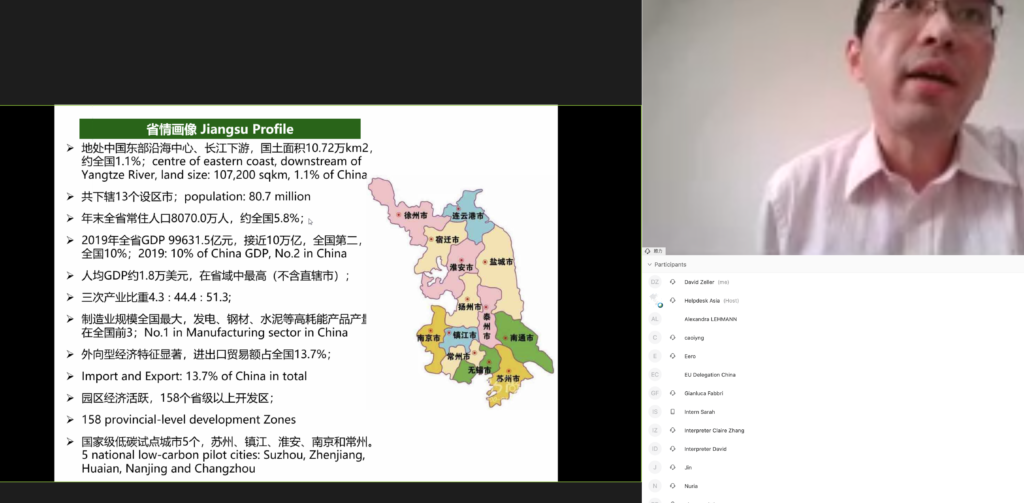
Case studies were presented on today’s call by the European cities of Bilbao (Spain) and Essen (Germany), and Chinese cities of Wuhan, Ningbo and Jiangsu Province. Experts explained challenges and achievements in the last decades of the cities’ transformation towards low-carbon. In general, they said that it’s the cities the ones who go ahead of the national governments, both in China and Europe.
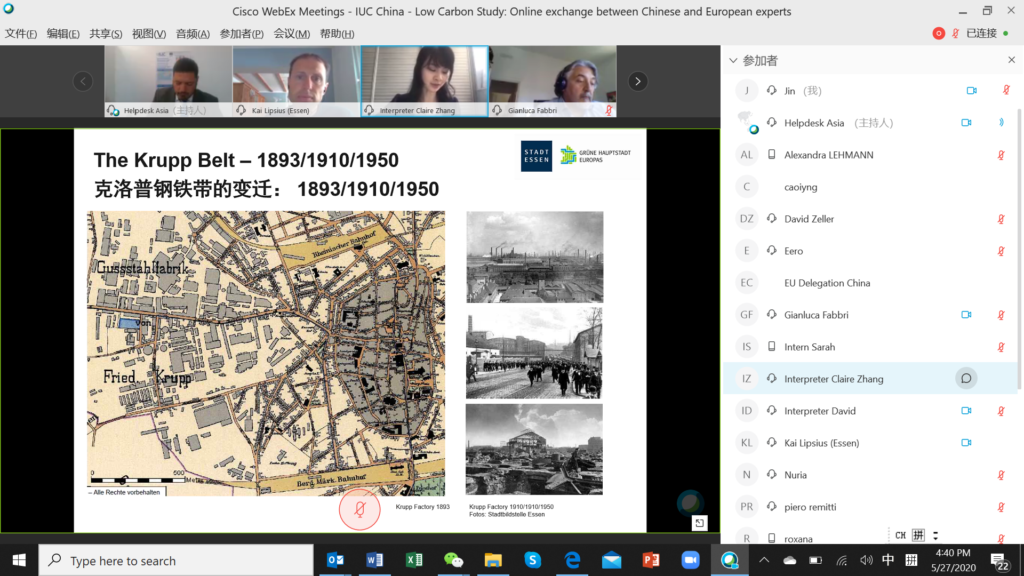
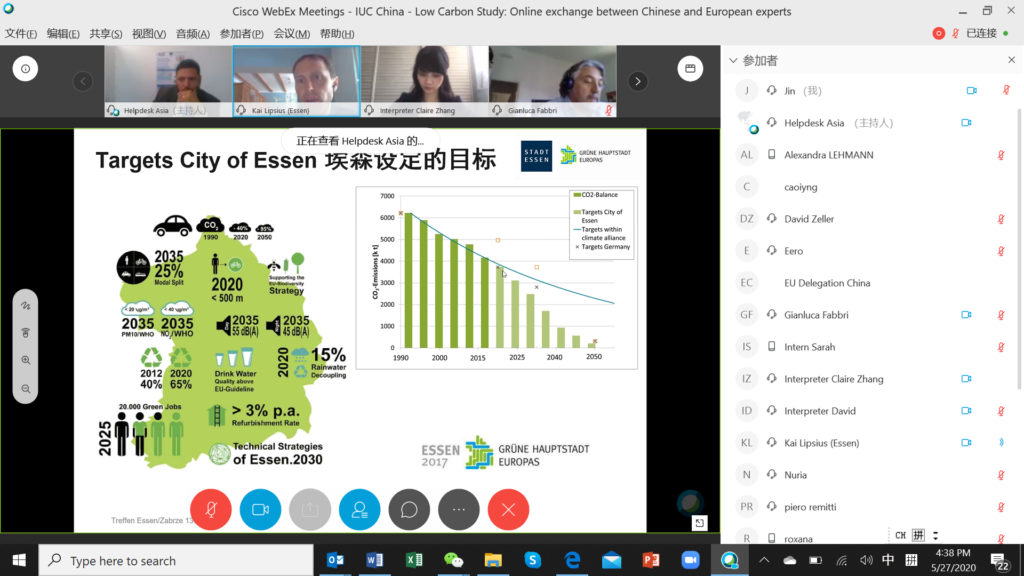
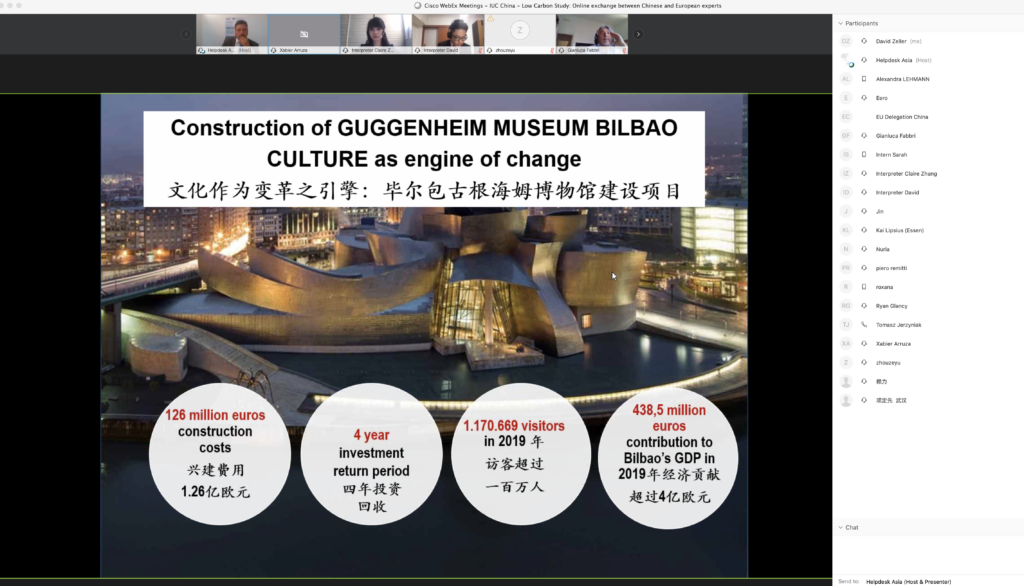
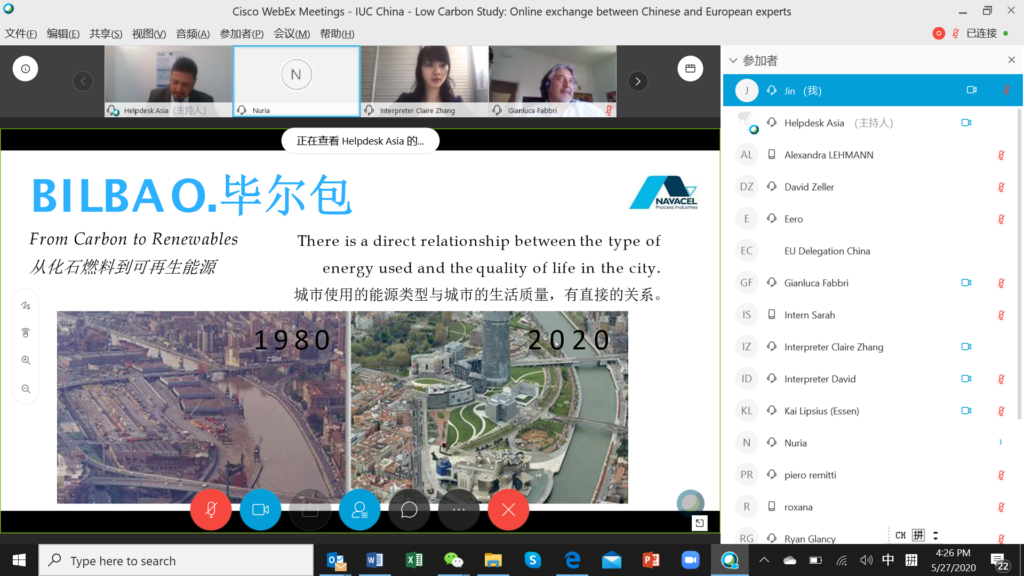
The role of businesses was emphasised in the case of Bilbao, in which Nuria Celorio from Navacel introduced the company’s business transformation in the last decades from carbon (the 1950s) through oil and gas (the 1980s) and now to wind and renewable energy. Xabier Arruza from Bilbao Urban and Cities Design explained the extraordinary transformation process of the city during the past decades. This worked on internal mobility, environmental and urban regeneration, and innovative public management. Xabier also explained the transformation of Abandoibarra, from an obsolete and run-down port area to an attractive promenade with cultural highlights (Guggenheim Museum), new green areas, hotels, shopping centres and residential apartments. Kai Lipsius from Essen explained the industrial transformation of the city, with massive coal production through mining that began in the early 19th century, and the subsequent heavy industry. The city has transformed from grey to green, with several major projects including the Krupp Belt development and the connection of the Emscher valley with Ruhr valley. With green areas and open spaces accounting for 54% of the city area, and with over 60,000 trees on the streets, Essen is the third-greenest major city in Germany and became the EU Green Capital 2017. Essen’s green development targets are beyond the national ones, making the city a frontrunner in Germany.
Experts shared views on the success factors towards low-carbon, including a long-term vision strategic plan based on a broad consensus of public-private partnerships. Xabier added that it’s crucial to have an innovative urban and economic regeneration and open governance model, as well as substantial and continued investment.
Experts also exchanged views on the expected effects of the Covid19 crisis to the low carbon transition efforts in cities in areas like public transportation were several people fear to use it due to contagious fear. Chinese experts also discussed the role of cities in the recovery process of the Covid19 crisis, mentioning that the reopening will maintain its sustainable development character. For example, Wuhan will not allow any new coal-energy projects and is fostering a model shift in transportation & mobility, including other means of mobility (cycling and new energy vehicles). In Wuhan’s construction sector, 100% of the projects compile with energy-saving / efficiency standards and 90% of the projects compile with green architecture construction requirements.
The presentations from these cities, as well as an overview of the EU-China Low Carbon City Study, can be found below:
Agenda_EN_IUC Asia – EU China Webinar Low Carbon 27.05.2020
01 Low Carbon Cities Study 27052020_v3_EN+CN
02 EU-China Low carbon Cities Joint Study0520_NCSC_EN+CN
03 Bilbao Urban & Cities Design – IUC- EN+CN
05_Essen_Lipsius_IUC_EU-China_Low_Carbon_EN+CN
06 Ningbo_Low Carbon Development_V2_CN-EN
07 Wuhan_Low Carbon Development_CN-EN
08 Jiangsu_Low Carbon Development_CN-EN
Some impressions from today’s online meeting: